|
I am a Ph.D. Scholar at IIIT Hyderabad, where I work on deep-learning, computer vision, multi-modal learning etc. My supervisors are Prof. C.V. Jawahar and Prof. Vinay Namboodiri . The primary focus of my Ph.D. has been to look into problems involving two naturally linked modalities, lip movements, and speech. I have been actively involved in multiple projects in this area and have published various papers in top conferences like CVPR, ACM Multimedia, etc. My core interests have been exploring how these modalities interact with each other and thus generating one from the other. Furthermore, one of my recent projects dealt with using both of these modalities to enhance human speech. Before joining IIITH, I worked as an intern under Prof. Santanu Chaudhury in CEERI, Pilani. During this period, I focused on image enhancement algorithms like image super-resolution, image inpainting, etc. I had published three papers during this stint. Email: radrabha.m@research.iiit.ac.in CV / Google Scholar / Twitter / Github / LinkedIn |

|
|
Most of my published papers focus on using concepts like self-supervision and try to exploit the natural correlation present between speech and lips. The image enhancement works that I did before joining IIITH did not also require manual labeling. Authors marked with a * have an equal contribution in the research done. |
|
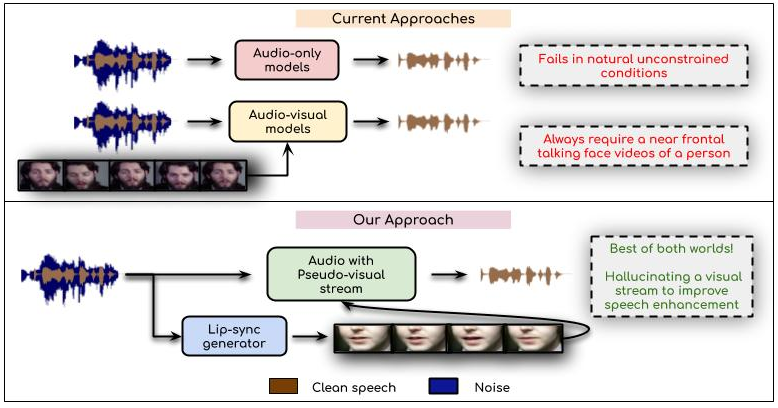
Sindhu Hegde*, K R Prajwal*, Rudrabha Mukhopadhyay*, Vinay Namboodiri, C.V. Jawahar, WACV, 2021 Project Page / Demo Video / Code / arXiv / CVF Abstract: In this work, we re-think the task of speech enhancement in unconstrained real-world environments. Current state-of-the-art methods use only the audio stream and are limited in their performance in a wide range of real-world noises. Recent works using lip movements as additional cues improve the quality of generated speech over ``audio-only" methods. But, these methods cannot be used for several applications where the visual stream is unreliable or completely absent. We propose a new paradigm for speech enhancement by exploiting recent breakthroughs in speech-driven lip synthesis. Using one such model as a teacher network, we train a robust student network to produce accurate lip movements that mask away the noise, thus acting as a ``visual noise filter". The intelligibility of the speech enhanced by our pseudo-lip approach is almost close (< 3\% difference) to the case of using real lips. This implies that we can exploit the advantages of using lip movements even in the absence of a real video stream. We rigorously evaluate our model using quantitative metrics as well as qualitative human evaluations. Additional ablation studies and a demo video in the supplementary material containing qualitative comparisons and results clearly illustrate the effectiveness of our approach. |

|
K R Prajwal*, Rudrabha Mukhopadhyay*, Vinay Namboodiri, C.V. Jawahar, ACM Multimedia, 2020 (Oral) Project Page / Demo Video / Code / Interactive Demo / arXiv / ACM DL Abstract: In this work, we investigate the problem of lip-syncing a talking face video of an arbitrary identity to match a target speech segment. Current works excel at producing accurate lip movements on a static image or videos of specific people seen during the training phase. However, they fail to accurately morph the lip movements of arbitrary identities in dynamic, unconstrained talking face videos, resulting in significant parts of the video being out-of-sync with the new audio. We identify key reasons pertaining to this and hence resolve them by learning from a powerful lip-sync discriminator. Next, we propose new, rigorous evaluation benchmarks and metrics to accurately measure lip synchronization in unconstrained videos. Extensive quantitative evaluations on our challenging benchmarks show that the lip-sync accuracy of the videos generated by our Wav2Lip model is almost as good as real synced videos. Please feel free to contact me for possible commercial usage of this project! We are in the process of filing a patent and also licinsing our model (we have a much better one than the one released). |

|
K R Prajwal*, Rudrabha Mukhopadhyay*, Vinay Namboodiri, C.V. Jawahar, CVPR, 2020 Project Page / Demo Video / Code / arXiv / CVF Abstract: Humans involuntarily tend to infer parts of the conversation from lip movements when the speech is absent or corrupted by external noise. In this work, we explore the task of lip to speech synthesis, i.e., learning to generate natural speech given only the lip movements of a speaker. Acknowledging the importance of contextual and speaker-specific cues for accurate lip-reading, we take a different path from existing works. We focus on learning accurate lip sequences to speech mappings for individual speakers in unconstrained, large vocabulary settings. To this end, we collect and release a large-scale benchmark dataset, the first of its kind, specifically to train and evaluate the single-speaker lip to speech task in natural settings. We propose a novel approach with key design choices to achieve accurate, natural lip to speech synthesis in such unconstrained scenarios for the first time. Extensive evaluation using quantitative, qualitative metrics and human evaluation shows that our method is four times more intelligible than previous works in this space. |
|
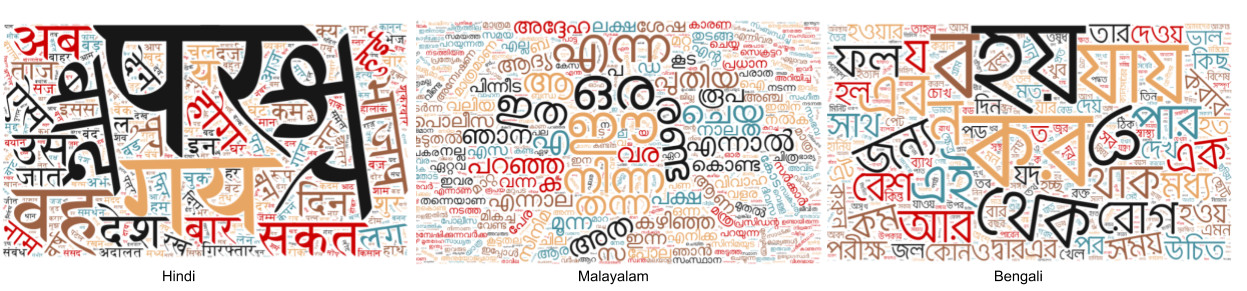
Nimisha Srivastava, Rudrabha Mukhopadhyay*, K R Prajwal*, C.V. Jawahar, LREC, 2020 Project Page / Dataset / Paper Abstract: India is a country where several tens of languages are spoken by over a billion strong population. Text-to-speech systems for such languages will thus be extremely beneficial for wide-spread content creation and accessibility. Despite this, the current TTS systems for even the most popular Indian languages fall short of the contemporary state-of-the-art systems for English, Chinese, etc. We believe that one of the major reasons for this is the lack of large, publicly available text-to-speech corpora in these languages that are suitable for training neural text-to-speech systems. To mitigate this, we release a 24 hour text-to-speech corpus for 3 major Indian languages namely Hindi, Malayalam and Bengali. In this work, we also train a state-of-the-art TTS system for each of these languages and report their performances. The collected corpus, code, and trained models are made publicly available. |

|
K R Prajwal*, Rudrabha Mukhopadhyay*, Jerin Philip , Abhishek Jha , Vinay Namboodiri, C.V. Jawahar, ACM Multimedia, 2019 (Oral) Project Page / Demo Video / Code / arXiv / ACM DL Abstract: In light of the recent breakthroughs in automatic machine translation systems, we propose a novel approach that we term as "Face-to-Face Translation". As today's digital communication becomes increasingly visual, we argue that there is a need for systems that can automatically translate a video of a person speaking in language A into a target language B with realistic lip synchronization. In this work, we create an automatic pipeline for this problem and demonstrate its impact on multiple real-world applications. First, we build a working speech-to-speech translation system by bringing together multiple existing modules from speech and language. We then move towards "Face-to-Face Translation" by incorporating a novel visual module, LipGAN for generating realistic talking faces from the translated audio. Quantitative evaluation of LipGAN on the standard LRW test set shows that it significantly outperforms existing approaches across all standard metrics. We also subject our Face-to-Face Translation pipeline, to multiple human evaluations and show that it can significantly improve the overall user experience for consuming and interacting with multimodal content across languages. |
|
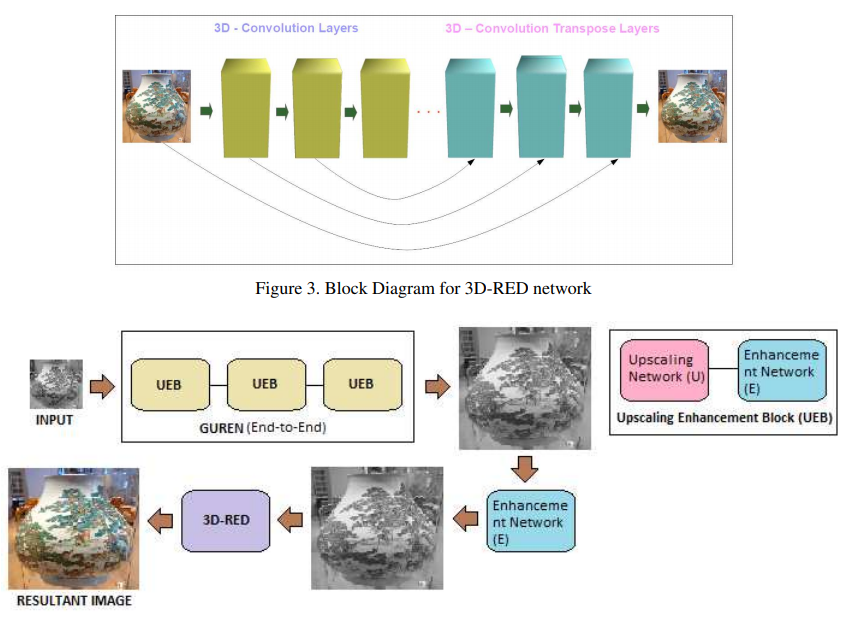
Manoj Sharma, Rudrabha Mukhopadhyay, Avinash Upadhyay, Sriharsha Koundinya, Ankit Shukla, Santanu Chaudhury, CVPR Workshops, 2018 Paper / Code Abstract: Convolutional neural network based architectures have achieved decent perceptual quality super resolution on natural images for small scaling factors (2X and 4X). However, image super-resolution for large magnification factors (8X) is an extremely challenging problem for the computer vision community. In this paper, we propose a novel Improved Residual based Gradual Up-Scaling Network (IRGUN) to improve the quality of the super-resolved image for a large magnification factor. IRGUN has a Gradual Upsampling and Residue-based Enhancment Network (GUREN) which comprises of series of Up-scaling and Enhancement blocks (UEB) connected end-to-end and fine-tuned together to give a gradual magnification and enhancement. Due to the perceptual importance of the luminance in super-resolution, the model is trained on luminance(Y) channel of the YCbCr image. Whereas, the chrominance components (Cb and Cr) channel is up-scaled using bicubic interpolation and combined with super-resolved Y channel of the image which is then converted to RGB. A cascaded 3D-RED architecture trained on RGB images is utilized to incorporate its inter-channel correlation. In addition to this, the training methodology is also presented in the paper. In the training procedure, the weights of the previous UEB are used in the next immediate UEB for faster and better convergence. Each UEB is trained on its respective scale by taking the output image of the previous UEB as input and corresponding HR image of the same scale as ground truth to the successive UEB. All the UEBs are then connected end-to-end and fine tuned. The IRGUN recovers fine details effectively at large (8X) magnification factors. The efficiency of IRGUN is presented on various benchmark datasets and at different magnification scales. |
|
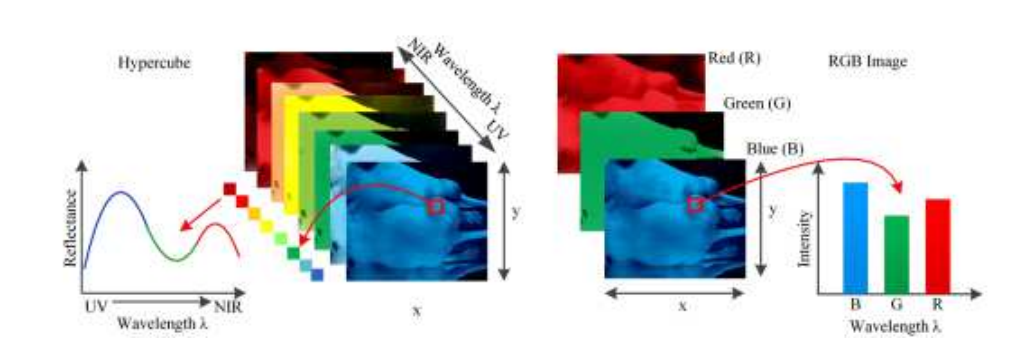
Sriharsha Koundinya, Himanshu Sharma, Manoj Sharma, Avinash Upadhyay, Raunak Manekar, Rudrabha Mukhopadhyay, Abhijit Karmakar, Santanu Chaudhury, CVPR Workshops, 2018 Paper Abstract: Hyperspectral cameras are used to preserve fine spectral details of scenes that are not captured by traditional RGB cameras, due to the gross quantization of radiance in RGB images. Spectral details provide additional information that improves the performance of numerous image based analytic applications, but due to high hyperspectral hardware cost and associated physical constraints, hyperspectral images are not easily available for further processing. Motivated by the success of deep learning for various computer vision applications, we propose a 2D convolution neural network and a 3D convolution neural network based approaches for hyper-spectral image reconstruction from RGB images. A 2D-CNN model primarily focuses on extracting spectral data by considering only spatial correlation of the channels in the image, while in 3D-CNN model the inter-channel co-relation is also exploited to refine the extraction of spectral data. Our 3D-CNN based architecture achieves state-of-the-art performance in terms of MRAE and RMSE. In contrast of 3D-CNN, our 2D-CNN based architecture also achieves performance near by state-of-the-art with very less computational complexity. |
|
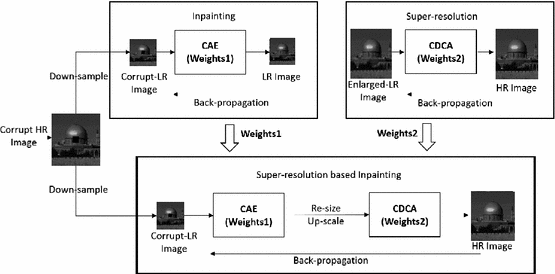
Manoj Sharma, Rudrabha Mukhopadhyay, Santanu Chaudhury, Brejesh Lall, NCVPRIPG, 2017 Paper Abstract: Image inpainting is an extremely challenging and open problem for the computer vision community. Motivated by the recent advancement in deep learning algorithms for computer vision applications, we propose a new end-to-end deep learning based framework for image inpainting. Firstly, the images are down-sampled as it reduces the targeted area of inpainting therefore enabling better filling of the target region. A down-sampled image is inpainted using a trained deep convolutional auto-encoder (CAE). A coupled deep convolutional auto-encoder (CDCA) is also trained for natural image super resolution. The pre-trained weights from both of these networks serve as initial weights to an end-to-end framework during the fine tuning phase. Hence, the network is jointly optimized for both the aforementioned tasks while maintaining the local structure/information. We tested this proposed framework with various existing image inpainting datasets and it outperforms existing natural image blind inpainting algorithms. Our proposed framework also works well to get noise resilient super-resolution after fine-tuning on noise-free super-resolution dataset. It provides more visually plausible and better resultant image in comparison of other conventional and state-of-the-art noise-resilient super-resolution algorithms. |
|
I have also presented our works in the form of demonstrations, at various conferences. Our demos has been well received and instrumental in increasing the visibility of the papers beyond the conferences we published them. |

|
K R Prajwal*, Rudrabha Mukhopadhyay*, Vinay Namboodiri, C.V. Jawahar, ECCV Demonstrations, 2020 Website / Demo Video / Abstract |

|
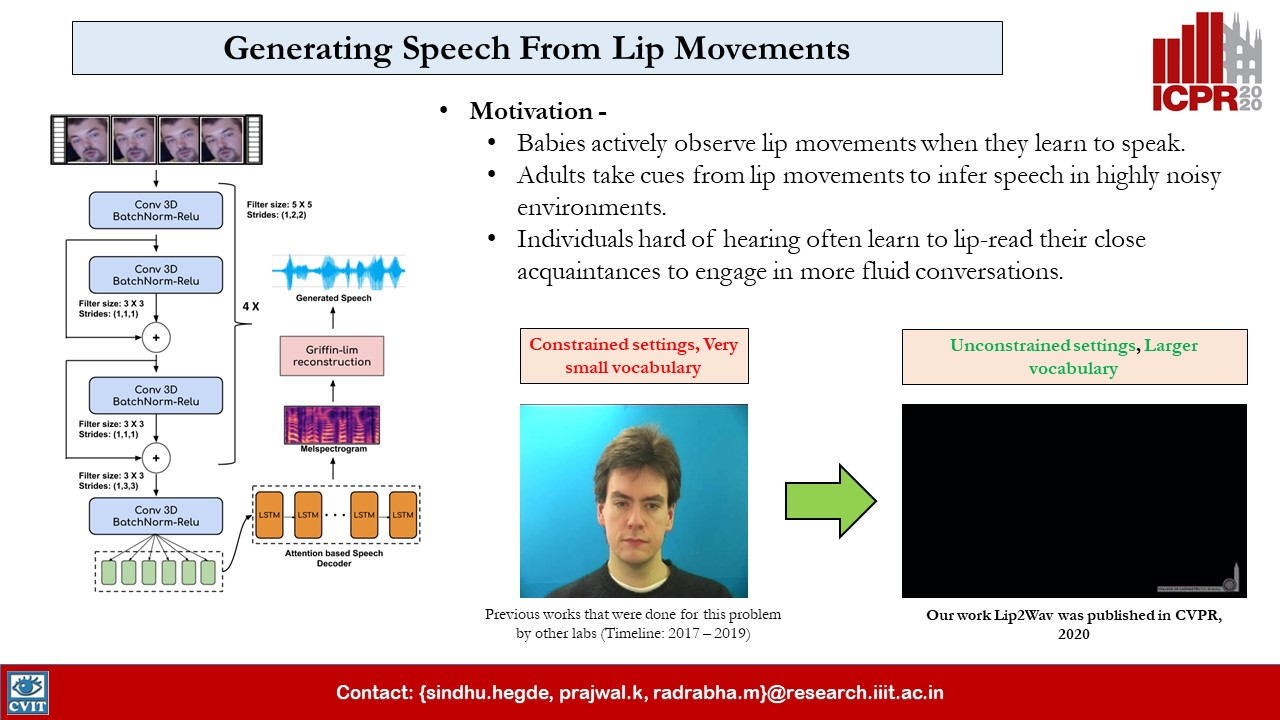
Rudrabha Mukhopadhyay*, K R Prajwal*, Sindhu Hegde*, Vinay Namboodiri, C.V. Jawahar, ICPR Demonstrations, 2020 Website / Demo Video / Demo Writeup |
|
Rudrabha Mukhopadhyay*, K R Prajwal*, Vinay Namboodiri, C.V. Jawahar, ICVGIP Vision-India Session, 2020 Video / Slides |
|
Rudrabha Mukhopadhyay*, K R Prajwal*, Vinay Namboodiri, C.V. Jawahar, NCVPRIPG Vision-India Session, 2019 Videos & Materials / Slides |
|
|

|
I received a grant to travel to Nice, France and attend ACM Multimedia, 2019. I had an oral presentation in the conference for our paper titled, "Towards Automatic Face-to-Face Translation". |
|
|

|
I acted as a reviewer in WACV, 2021 and reviewed two papers for the conference organizers. |
|
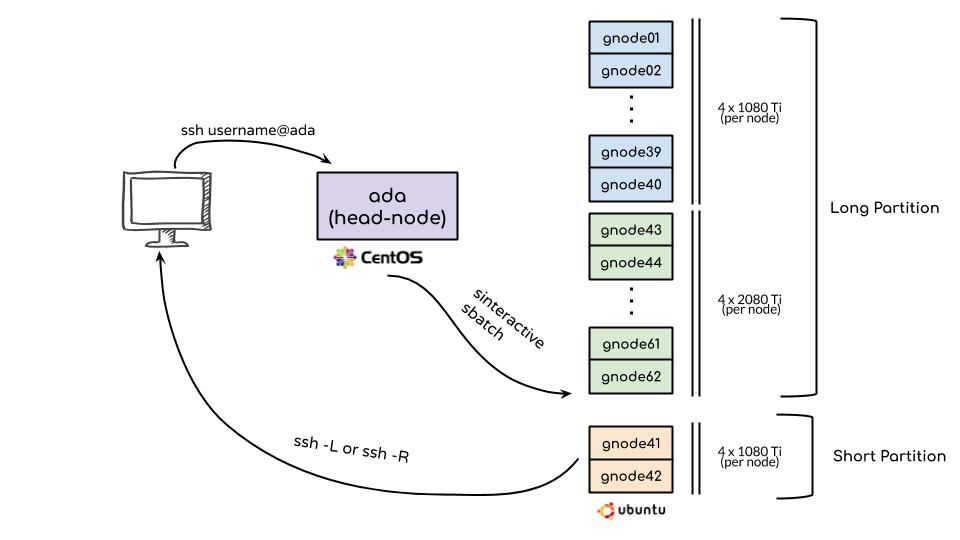
I am a student system administrator for the HPC cluster of IIIT-Hyderabad. Our cluster is known as ADA and contains 252 GPUs and 2520 CPUs. I currently manage the shared resources needed to be allocated to around 400 users in the cluster. I was instrumental in acquiring new storage devices for the cluster and the subsequent shifting of large amounts of data. I am also a part of the high-level policymaking group overseeing the general operations of the cluster. |

|
I have regularly donated blood since July, 2014 after I turned 18. According to the American Red Cross, one donation can save as many as three lives. I am truly committed to this cause and hope to continue the practice in future. |